- July 4, 2023
- Saloni Kabra
- 0
Living with bipolar disorder can be a rollercoaster ride, impacting every aspect of a person’s life. From extreme highs to debilitating lows, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of bipolar disorder to effectively manage and navigate this complex condition. In this blog, we will delve into the different types of bipolar disorder, explore the symptoms associated with each phase, and shed light on the diagnostic process.
Emoneeds, a platform dedicated to mental health services, offers tailored support to those living with bipolar disorder, assisting them in their journey toward stability and well-being.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Bipolar Disorder
Definition and Explanation
Bipolar disorder is a mental health condition characterized by intense mood swings known as mood episodes. These episodes can range from manic highs, where individuals experience heightened energy and euphoria, to depressive lows, marked by deep sadness and despair. It is important to recognize that bipolar disorder is not a fleeting change in mood but a chronic condition that requires careful management.
Prevalence and Impact
Bipolar disorder affects a significant number of individuals worldwide. According to studies, approximately 2.8% of the global population is affected by bipolar disorder. The impact of this condition extends beyond the individual, often straining relationships, hindering daily functioning, and impeding overall quality of life. Understanding the intricacies of bipolar disorder can help individuals and their support networks provide the necessary care and support.
Types of Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar I Disorder
The presence of manic episodes characterizes bipolar I disorder. During manic episodes, individuals may exhibit an elevated mood, increased energy levels, decreased need for sleep, and engage in impulsive or risky behaviors. These manic episodes can be intense and may result in significant consequences if left unmanaged.
Bipolar II Disorder
Bipolar II disorder differs from bipolar I disorder in that it is characterized by hypomanic episodes rather than full-blown manic episodes. Hypomanic episodes are less severe but can still lead to noticeable changes in behavior and mood. Depressive episodes, similar to those experienced in bipolar I disorder, are also present in bipolar II disorder.
Cyclothymic Disorder
Cyclothymic disorder is a milder form of bipolar disorder characterized by chronic and fluctuating mood changes. Individuals with cyclothymic disorder experience periods of hypomanic and depressive symptoms but not to the same degree as in bipolar I or bipolar II disorder. These mood shifts can last for extended periods, sometimes spanning years.
Symptoms of Bipolar Disorder
Manic Episodes
During manic episodes, individuals experience a whirlwind of emotions and behaviors that can significantly impact their lives. They often exude an inflated sense of self-confidence, feeling invincible and unstoppable. Their speech becomes rapid and frenzied as if their thoughts are racing a mile a minute. This increased energy manifests in impulsive behaviors, such as excessive spending sprees or reckless driving.
Additionally, they may require less sleep than usual, finding themselves awake and active for extended periods. It becomes challenging for them to maintain focus and concentrate on tasks, as their thoughts constantly jump from one idea to another. This heightened state of agitation and restlessness can lead to an increased propensity for taking risks, both physically and emotionally.
Depressive Episodes
Bipolar disorder’s depressive episodes bring deep sadness and despair, accompanied by emptiness and hopelessness. Joyful activities lose their appeal, appetite changes occur (either loss or gain), and sleep disturbances worsen emotional distress. Fatigue and low energy levels make simple tasks overwhelming. Concentration becomes difficult due to negative thoughts and self-criticism. In severe cases, self-harm or suicide may be contemplated, emphasizing the need for timely support.
Understanding the symptoms associated with both manic and depressive episodes is essential in recognizing the various facets of bipolar disorder. By being aware of these signs, individuals, their loved ones, and mental health professionals can collaborate to develop effective strategies and interventions that promote stability, emotional well-being, and a higher quality of life.
Diagnosis of Bipolar Disorder
Professional Evaluation
Diagnosing bipolar disorder requires the expertise and guidance of mental health professionals. They possess the knowledge and skills necessary to conduct a comprehensive evaluation, taking into account various factors to reach an accurate diagnosis. This evaluation typically entails a detailed assessment of the individual’s medical history, a thorough examination of their symptoms, and discussions about their family history. Open and honest communication during this evaluation process is crucial as it lays the foundation for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnostic Criteria
To diagnose bipolar disorder, mental health professionals refer to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), which provides specific criteria for differentiating bipolar I disorder, bipolar II disorder, and cyclothymic disorder. These criteria outline the key characteristics and features of each type of bipolar disorder. During the evaluation, mental health professionals carefully assess the duration, severity, and frequency of mood episodes experienced by the individual. By aligning the individual’s experiences with the diagnostic criteria, mental health professionals can determine the most appropriate diagnosis.
Differential Diagnosis
Accurately diagnosing bipolar disorder can be complex due to the presence of overlapping symptoms with other mental health conditions. Mental health professionals must meticulously evaluate and rule out other potential causes of mood swings, such as medical conditions or substance abuse. This process of differential diagnosis involves a comprehensive assessment and exploration of various factors to ensure an accurate diagnosis. By ruling out other potential causes, mental health professionals can confidently attribute the individual’s experiences to bipolar disorder, facilitating the development of an effective treatment plan.
The diagnostic process for bipolar disorder is a collaborative effort between the individual and their mental health professionals. By providing accurate and detailed information, individuals can contribute to a comprehensive evaluation that leads to an accurate diagnosis. This diagnosis forms the foundation for creating a tailored treatment plan that addresses their unique needs and helps them effectively manage their bipolar disorder.
Seeking Help and Treatment Options
Recognizing the Need for Help
Developing self-awareness is vital in recognizing the signs and symptoms of bipolar disorder. If you or someone you know is experiencing significant mood swings that disrupt daily life, seeking professional help is essential. It is important to remember that reaching out for assistance is not a sign of weakness but rather a courageous step towards managing the condition and improving overall well-being. By acknowledging the need for help, individuals can embark on a path toward finding the support they require.
Treatment Approaches
Bipolar disorder is a complex condition that necessitates a comprehensive and multidimensional treatment approach. Treatment options often involve a combination of medication and therapy. Mood stabilizers, prescribed by healthcare professionals, can play a crucial role in managing mood swings and preventing episodes. These medications help restore stability and create a foundation for individuals to engage in other therapeutic interventions.
Therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and psychoeducation, is another integral component of bipolar disorder treatment. CBT focuses on identifying and modifying negative thought patterns and behaviors, providing individuals with valuable coping strategies and tools to manage their condition effectively. Psychoeducation equips individuals with knowledge about bipolar disorder, its symptoms, triggers, and warning signs, enabling them to better understand their experiences and make informed decisions regarding their treatment.
Lifestyle Management
Alongside professional treatment, lifestyle factors play a significant role in managing bipolar disorder. Making positive changes in daily routines and habits can have a profound impact on stabilizing mood and reducing the frequency of episodes. Establishing a regular sleep schedule and prioritizing adequate rest can help regulate circadian rhythms, promoting overall well-being. Engaging in regular physical activity, such as exercise or outdoor activities, has been shown to have mood-stabilizing effects and improve overall mental health.
Practicing stress reduction techniques, such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in creative outlets, can assist individuals in managing stressors that may trigger mood swings. Additionally, maintaining a balanced diet, rich in nutrients, and avoiding excessive consumption of stimulants like caffeine or alcohol, can contribute to overall stability and well-being.
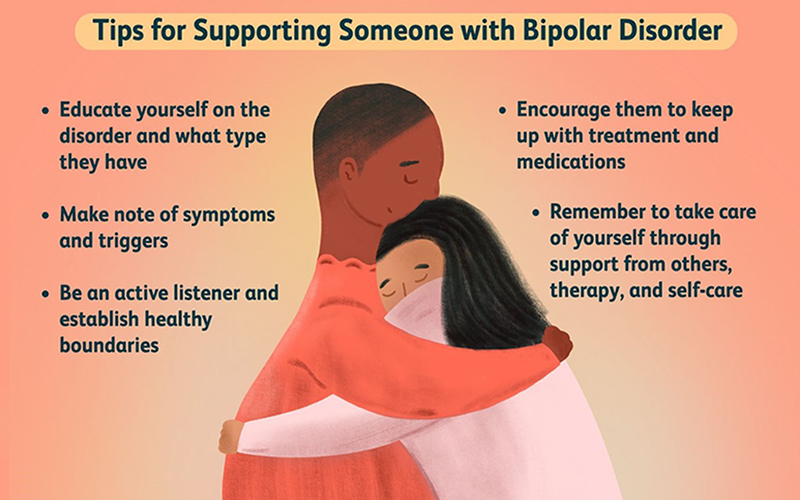
Building a strong support network is also crucial in managing bipolar disorder. Seeking support from loved ones, friends, and support groups can provide a sense of understanding, validation, and encouragement. Sharing experiences with others who have similar challenges can foster a sense of community and reduce feelings of isolation.
How Does Emoneeds Help?
Emoneeds offers a supportive environment for individuals living with bipolar disorder. Their team of expert psychiatrists, clinical psychologists, and therapists work collaboratively to provide holistic care, tailored to individual needs. Emoneeds offers a range of services, including online therapy, medication management, cognitive rehabilitation therapy (CRT), and social skills therapy (SST). By utilizing their expertise and utilizing the convenient online platform, individuals can access high-quality mental health care, making their journey toward stability and well-being more accessible.
By combining professional treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and a supportive network, individuals living with bipolar disorder can effectively manage their condition and lead fulfilling lives. Each person’s journey is unique, and it is important to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop an individualized treatment plan that meets their specific needs. With the right support, individuals with bipolar disorder can achieve stability, find resilience, and live a life filled with hope and possibility.
Conclusion
Bipolar disorder is a complex mental health condition that requires a comprehensive understanding of its types, symptoms, and diagnosis. By recognizing the different types of bipolar disorder and their unique features, individuals can seek appropriate help and develop effective strategies for managing their condition. With professional guidance, treatment options, and a supportive network, individuals with bipolar disorder can navigate their journey toward stability, improved well-being, and a fulfilling life.
Remember, seeking professional help is the first step towards understanding and managing bipolar disorder effectively. Together, we can provide support, foster resilience, and empower individuals to lead productive and fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by bipolar disorder.
FAQ
What are the 4 stages of bipolar?
Bipolar disorder has four main stages:
- Mania: Extreme highs in mood, energy, and activity levels.
- Hypomania: Less severe than mania but still elevated mood and increased energy.
- Depression: Intense lows in mood, energy, and motivation.
- Stability: Periods between episodes where mood and energy levels are balanced.
These stages can vary in intensity and duration for each person. Treatment, including medication and therapy, aims to manage symptoms and promote stability.
What are the 5 common symptoms of bipolar?
The five common symptoms of bipolar disorder include mood swings, ranging from manic highs to depressive lows, which can affect daily life. Patients may experience intense feelings of happiness, energy, or irritability during manic episodes, followed by periods of sadness, fatigue, or hopelessness during depressive episodes. Changes in sleep patterns, appetite, and concentration are also common. Some individuals may engage in risky behaviors or have difficulty in relationships. Seeking medical advice is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
How do I know if I’m bipolar?
If you wonder if you’re bipolar, look for mood swings. Bipolar disorder involves extreme mood changes, from high (mania or hypomania) to low (depression). Watch for periods of high energy, racing thoughts, and reckless behavior during mania. In depression, you may feel hopeless, tired, and lose interest in activities. Pay attention to these shifts and talk to a doctor if you notice them interfering with daily life. A proper diagnosis can lead to effective treatment and improved quality of life.
Is bipolar A Genetic Disease?
Yes, bipolar disorder can have a genetic component. Studies indicate that having a family history of the disorder increases one’s risk. Genetic factors can influence the likelihood of developing bipolar disorder, although environmental factors also play a role. While not everyone with a family history will develop the condition, it’s essential to be aware of the genetic predisposition. Understanding the genetic link can help individuals and families recognize potential signs and symptoms early on, leading to timely interventions and better management strategies. If you have concerns about your genetic risk for bipolar disorder, consulting with a healthcare professional can provide valuable insight and guidance.
When does bipolar first start?
Bipolar disorder typically starts in late adolescence or early adulthood, but it can also emerge during childhood or later in life. Symptoms often appear in the late teens or early twenties, although they can manifest at any age. It’s essential to recognize early signs like drastic mood swings, changes in energy levels, and disruptions in daily activities. If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms, seeking help from a healthcare professional is crucial for proper diagnosis and management.